What is Risk Analysis? – Detailed Explanation
Risk analysis is a process used to identify, assess, and prioritize risks in order to manage and mitigate their potential impact on an organization or project. It involves the systematic examination of factors that could cause uncertain outcomes, evaluating the likelihood of their occurrence, and the extent of their possible effects. This analysis helps decision-makers to make informed choices, prioritize actions, and allocate resources effectively to reduce the likelihood of undesirable events or to prepare for their consequences.
Risk analysis is a critical component of risk management and is applied across various fields, including finance, insurance, public health, safety, and project management, among others.
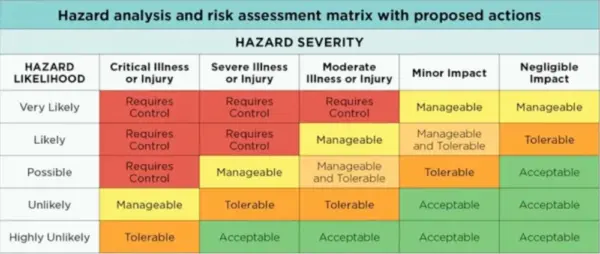
Table of Contents
Understanding Risk Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide for Businesses
![]()
Risk analysis is a fundamental process that businesses employ to identify, assess, and manage potential threats that could compromise their operations, assets, or objectives. It is a proactive measure that allows organizations to prepare for and mitigate the impacts of various risks, ensuring the continuity and stability of their business activities. Understanding risk analysis is crucial for any business that aims to navigate the complex landscape of uncertainties it faces in today’s dynamic environment.
At its core, risk analysis involves a systematic approach to recognizing the hazards that could negatively affect a company’s ability to function effectively. These risks can be diverse, ranging from financial uncertainties, legal liabilities, management errors, accidents, natural disasters, and strategic missteps to cybersecurity threats. By identifying these potential issues, businesses can prioritize them based on the likelihood of occurrence and the severity of their impact.
Once risks are identified, the next step in risk analysis is to evaluate them. This evaluation is typically quantitative, qualitative, or a combination of both. Quantitative analysis uses numerical values and statistical models to estimate the probability and potential impact of risks, providing a more objective basis for decision-making. Qualitative analysis, on the other hand, relies on judgment and experience to assess risks, often using rating systems to categorize and prioritize them. This step is critical as it helps businesses understand which risks are acceptable and which require immediate attention.
After evaluating the risks, businesses must develop strategies to manage them. This involves deciding whether to accept, avoid, transfer, or mitigate each risk. Accepting a risk means acknowledging it without taking action, a decision usually reserved for low-priority risks. Avoiding a risk entails changing plans or procedures to eliminate the threat entirely. Transferring risk often involves purchasing insurance or outsourcing certain operations to third parties. Mitigating risk is perhaps the most common strategy, involving steps to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk.
Effective risk management also includes monitoring and reviewing the risks on an ongoing basis. The business environment is ever-changing, and new risks can emerge while existing ones evolve. Regular monitoring ensures that the risk analysis remains relevant and that the risk management strategies are effective. This continuous process enables businesses to adapt their risk management practices in response to internal and external changes.
Moreover, risk analysis is not just about preventing negative outcomes; it also offers businesses the opportunity to identify potential opportunities that risk-taking can present. By understanding the full spectrum of risks, companies can make informed decisions that balance potential downsides with the upsides of pursuing innovative strategies and entering new markets.
In conclusion, risk analysis is an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to safeguard their interests and ensure long-term success. It provides a structured framework for identifying, evaluating, and managing the uncertainties that are inherent in any business venture. By embracing risk analysis, businesses can not only protect themselves against potential threats but also position themselves to take advantage of opportunities that arise from the ever-present nature of risk. As such, understanding and implementing risk analysis is a comprehensive guide for businesses to navigate the complexities of the modern world with confidence and strategic foresight.
Types of Risk Analysis
![]()
Risk analysis is a process that involves identifying and assessing factors that could negatively affect the success of a project, business, or investment. There are various types of risk analysis that can be performed, each focusing on different aspects and employing different methodologies. Here are some common types of risk analysis:
1. Qualitative Risk Analysis:
- Checklist Analysis: Involves using a pre-defined list of potential risks to evaluate a project or investment.
- Expert Judgment: Relies on the experience and intuition of experts to assess risks.
- Delphi Technique: A structured communication technique where a panel of experts answers questionnaires in two or more rounds.
2. Quantitative Risk Analysis:
- Probabilistic Risk Assessment: Uses probability distributions to represent the uncertainty of risk.
- Monte Carlo Simulation: A computational algorithm that uses random sampling to obtain numerical results.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Studies how different values of an independent variable affect a particular dependent variable under a given set of assumptions.
- Scenario Analysis: Evaluates the expected value of a given investment or project over different scenarios.
3. Financial Risk Analysis:
- Credit Risk Analysis: Assesses the likelihood of a borrower defaulting on a loan.
- Market Risk Analysis: Evaluates the risk of investments due to market fluctuations.
- Liquidity Risk Analysis: Analyzes the risk that an entity will not be able to meet its short-term financial obligations.
- Interest Rate Risk Analysis: Assesses the risk of changes in interest rates affecting investment values.
4. Strategic Risk Analysis:
- PESTLE Analysis (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental): Reviews external factors that can affect the success of a project or business.
- SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats): Identifies internal and external factors that can affect the organization’s ability to achieve its objectives.
5. Operational Risk Analysis:
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): A step-by-step approach for identifying all possible failures in a design, manufacturing, or assembly process.
- Root Cause Analysis: Focuses on identifying the underlying reasons why a problem occurred.
- Business Impact Analysis: Evaluates the potential effects of an interruption to critical business operations due to a disaster, accident, or emergency.
6. Project Risk Analysis:
- Critical Path Method (CPM): Identifies the longest stretch of dependent activities and measures the time required to complete them.
- Earned Value Analysis: Measures project performance against the project plan.
- Risk Register: A tool used to document risks, their severity, and the actions steps to be taken.
7. Compliance Risk Analysis:
- Regulatory Compliance Analysis: Evaluates the risk of not adhering to laws, regulations, guidelines, or specifications relevant to the business or project.
- Legal Risk Analysis: Assesses the risk of legal actions due to non-compliance, contracts, or other legal matters.
8. Environmental Risk Analysis:
- Ecological Risk Assessment: Evaluates the potential harm that a human activity may pose to natural resources.
- Climate Risk Analysis: Assesses the risk associated with climate change and its impact on operations and assets.
9. Health and Safety Risk Analysis:
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment (HIRA): Aims to identify and assess the risk associated with workplace hazards.
- Occupational Health and Safety Assessment: Analyzes risks related to employee health and safety in the workplace.
10. Technological Risk Analysis:
- Cybersecurity Risk Assessment: Identifies, estimates, and prioritizes the risk to organizational operations caused by cyber threats.
- IT Risk Assessment: Evaluates risks related to the use, ownership, operation, involvement, influence, and adoption of IT within an organization.
Each type of risk analysis aims to help organizations understand the risks they face, quantify them where possible, and create plans to mitigate or manage these risks effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
![]()
1. What is risk analysis?
Risk analysis is the process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks to an organization’s capital and earnings. It involves quantifying the probability and potential impact of adverse events and is an essential part of risk management.
2. Why is risk analysis important?
Risk analysis is important because it helps organizations to understand the potential threats to their operations, financial performance, and reputation. It enables proactive management of risks, ensuring that they are identified, assessed, and mitigated before they can cause significant harm.
3. What are the key components of risk analysis?
The key components of risk analysis typically include risk identification, risk assessment (which includes likelihood and impact analysis), risk prioritization, and the development of risk mitigation strategies.
4. What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative risk analysis?
Qualitative risk analysis involves assessing risks based on subjective criteria, such as the experience or intuition of the risk analyst, and often uses categories like high, medium, or low to describe risk levels. Quantitative risk analysis, on the other hand, uses numerical values and statistical models to measure risk probability and impact.
5. Can risk analysis help in decision-making?
Yes, risk analysis is a crucial tool in decision-making as it provides a structured approach to evaluating the uncertainties associated with different options. It helps decision-makers to understand the potential downsides and to make more informed choices.
6. How often should risk analysis be performed?
The frequency of risk analysis depends on the nature of the organization and its environment. It is typically performed on a regular basis, such as annually, or whenever there are significant changes to the business, its operations, or its external environment.
7. What are some common methods used in risk analysis?
Some common methods include failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA), hazard and operability study (HAZOP), root cause analysis, fault tree analysis, and Monte Carlo simulation.
8. Who should be involved in risk analysis?
Risk analysis should involve stakeholders from various parts of the organization, including senior management, finance, operations, IT, and any other areas where risks may emerge. It can also benefit from the involvement of external experts and consultants.
9. How do you prioritize risks in risk analysis?
Risks are typically prioritized based on their potential impact and the likelihood of occurrence. This can be done using tools such as a risk matrix, which plots risks on a grid to identify which ones require immediate attention and resources.
10. What is a risk matrix?
A risk matrix is a graphical tool used to classify risks according to their severity and likelihood. It helps in visualizing and prioritizing risks to aid in decision-making.
11. What is the difference between risk analysis and risk assessment?
Risk analysis is a broader term that encompasses the entire process of risk evaluation, including risk identification, assessment, and prioritization. Risk assessment is a subset of risk analysis, focusing specifically on evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified risks.
12. How does risk analysis relate to risk management?
Risk analysis is a core component of risk management. It provides the necessary information to develop risk management strategies and make decisions about risk mitigation, transfer, acceptance, or avoidance.
13. Can risk analysis eliminate all risks?
No, risk analysis cannot eliminate all risks. Its purpose is to understand and manage risks effectively, not to eliminate them entirely. Some risks are inherent to business activities and can only be mitigated or managed, not completely removed.
14. Does risk analysis differ by industry?
Yes, risk analysis can vary significantly by industry due to different regulatory environments, operational processes, market conditions, and other industry-specific factors.
15. What are some challenges in conducting risk analysis?
Challenges in risk analysis may include data limitations, difficulty in quantifying certain risks, biases in risk perception, rapidly changing risk landscapes, and the complexity of modeling interdependent risks.
Conclusion
![]()
Risk analysis is the process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks to an organization’s capital and earnings. It involves quantifying the probability of adverse events and their potential impacts, with the aim of enabling informed decision-making and risk mitigation strategies. The ultimate goal of risk analysis is to manage risk effectively to minimize the negative consequences for an organization while maximizing opportunities.
Originally posted 2022-09-19 01:34:27.
